What is it?
Abnormal growth of normal cells with no proper development. They usually grow slowly and don’t invade the surrounding structures or spread to other organs. They compress the surrounding brain tissue and cause symptoms due to this. With modern technological advances in the operative techniques they can be removed completely.
What are the symptoms?
They can be life threatening since they compress the surrounding brain tissue and increase the pressure inside the skull. In this context the term benign is a misnomer.
They can present with:
- Visual problems
- Hearing impairment
- Balance problems
- 4. Memory impairment
- 5. Changes in mental ability
- 6. Seizures
- 7. Change in smell perception
- 8. Headache and vomiting
- 9. Facial paralysis
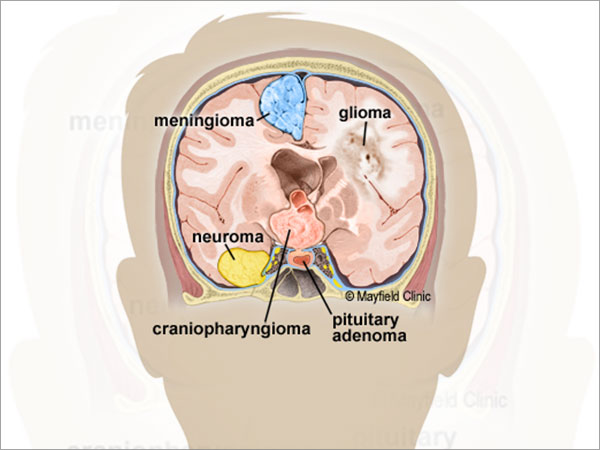
What are the types?
- 1. Meningioma: tumor from the coverings of brain
- 2. Schwanomma: tumor from the coverings of nerve
- 3. Pituitary adenoma: tumor from pituitary gland
- 4. Hemangioblastoma: tumor from blood vessels
- 5. Craniopharyngioma: tumor from remnants of nasal cavity in the brain
- 6. Others like dermoid and epidermoid
 |
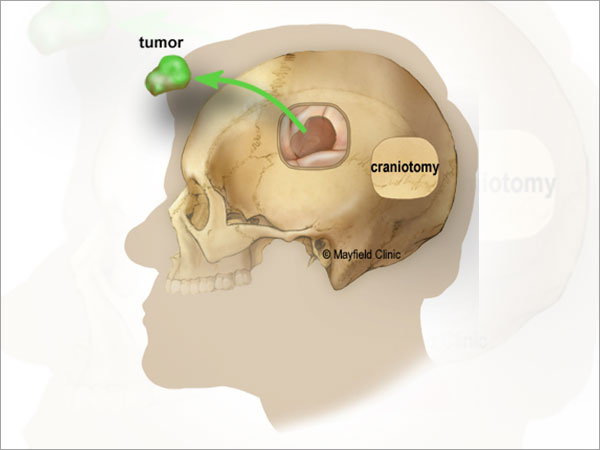 |
How are they treated?
Unfortunately there are no medicines to cure this condition. Surgery is the main stay. It entails removing a piece of skull bone, excising the tumor completely and replacing the bone back. Medicines are given to reduce the brain swelling and to prevent seizures.
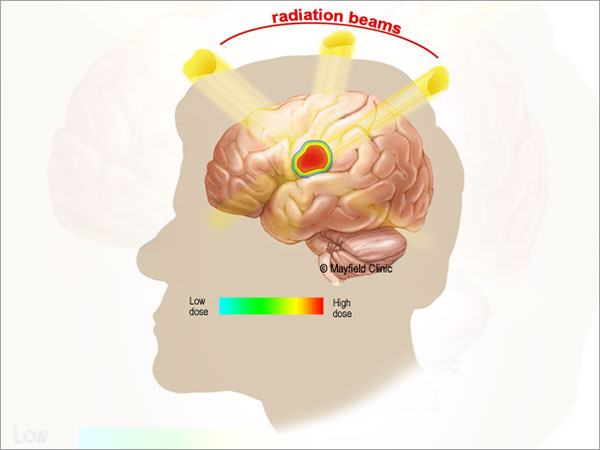
Radiation therapy is sometimes needed to treat residual or recurrent tumor and in people who are not fit for surgery. These include conventional radiotherapy, gamma knife, cyber knife and proton beam therapy.
 |
 |


