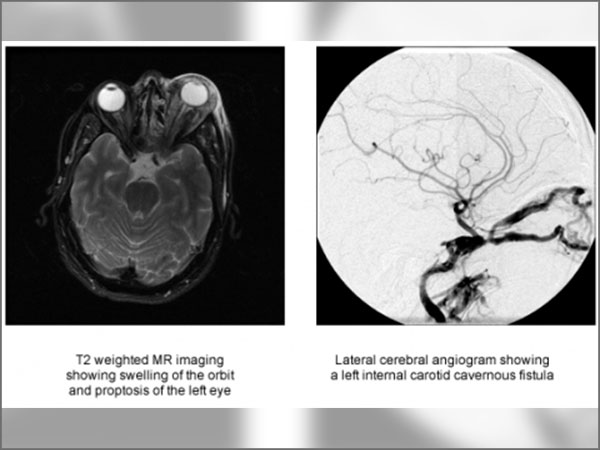
What is CCF?
It is an abnormal connection between the carotid artery or its branches and a large vein called cavernous sinus. This sinus is located behind the eye and receives blood from it and the brain.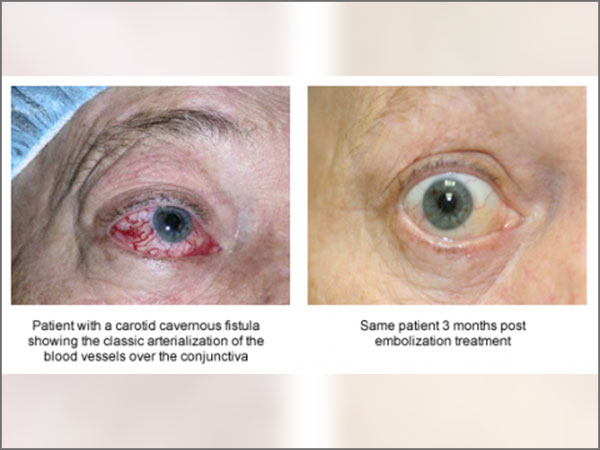
Types of CCF
- Spontaneous: due to rupture of the carotid artery aneurysm into the cavernous sinus.
- Traumatic following a head injury either blunt or penetrating.
What are the symptoms?
Patients present with classic triad of
- Chemosis: red eye
- Pulsatile exophthalmos: abnormal protrusion of the eye
- Ocular bruit: blood flow sounds
Other symptoms are
- proptosis: protrusion of the entire eye
- Diplopia: double vision
- Visual loss: blindness
How is it diagnosed?
- history
- clinical examination
- CT and MRI
- Cerebral angiography
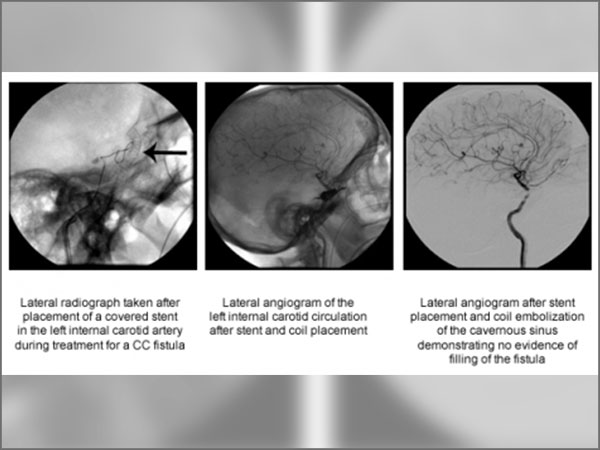
How is it treated?
- there is no medical treatment
- Endovascular treatment
- Deploying detachable balloons
- Covered stents
- Stent assisted coiling
- Surgical: opening the skull and occluding the carotid artery proximal and distal to the fistula. This sis followed by cerebral revascularization by joining the vessels of the face and those of t brain.