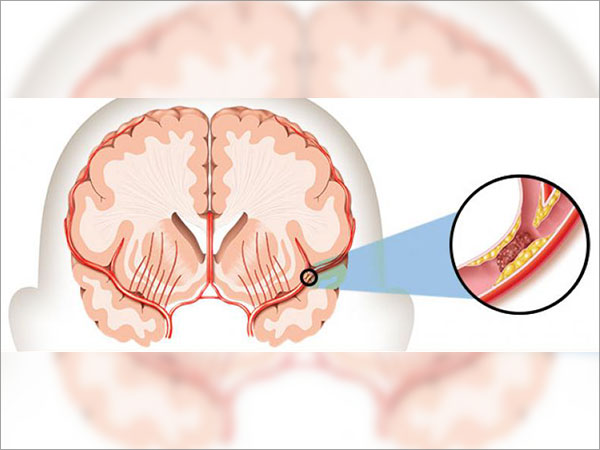
Stroke is a common cause of death and is the leading cause of morbidity. It occurs when a blood vessel that carries oxygen and nutrients to the brain is either blocked by a clot or bursts. This results in cessation of blood supply to that part of brain and the brain cells die.
What are the types of stroke?
When a blood clot obstructs the flow of blood in the blood vessel it is called ischemic stroke. With the blood vessel rupturing and preventing blood flow it is called hemorrhagic stroke. A temporary clot in the blood vessel causes transient ischemic attack.
What are the effects of stroke?
Brain is an extremely complex organ that controls various body functions. The effects of stroke depend on several factors including the area of obstruction and the amount of brain tissue affected. Stroke affecting one side of the brain results in neurological complications on the opposite side of the body.
What are the symptoms?
- Trouble with speaking and understanding
- Paralysis and numbness of the face, arm or leg
- Trouble with seeing with on or both eyes
- Headache
- Trouble with walking
When to see a doctor?
Immediate attention should be sought if one suspects signs and symptoms of stroke. One should think FAST and do the needful.
- FACE: ask the patient to smile.
- ARMS: ask the patient to raise arms and see for any weakness
- SPEECH: ask the patient for simple questions and see for any slur
- TIME: if any of these are present rush him to the hospital.
DO NOT WAIT. EVERY MINUTE COUNTS. The longer a stroke goes untreated, the greater the potential for brain damage and disability.
What are the causes of stroke?
- Ischemic stroke: caused by a blocked vessel. They form 80% of strokes. They can be
- Thrombotic: when blood clot forms in one of the blood vessels to brain.
- Embolic: when the clot forms in the heart and migrates to brain.
- Hemorrhagic stroke: occurs when a blood vessel in the brain ruptures, due to
- Uncontrolled high blood pressure.
- Overtreatment with blood thinners
- Weak spots in blood vessels called aneurysms.
- Less common cause is rupture of abnormal tangle of blood vessels called arteriovenous malformation.
Hemorrhage can be into the brain parenchyma and is called intra cerebral hemorrhage. It is usually caused by bleeds due to high blood pressure, blood thinners and vascular malformations. Sometimes it can be due to sub arachnoid hemorrhage where bleeding occurs into a space between the brain and skull. This is usually due to bursting of an aneurysm, a weak spot in the blood vessel.
Transient Ischemic attack: it is otherwise called a mini stroke. Here the symptoms are reversible since there is a temporary decrease in blood flow to brain. There is no permanent brain damage but this episode of TIA has to be taken seriously and immediate treatment has to be sought.
What are the risk factors?
- Obesity and overweight
- Physical inactivity
- Binge drinking
- Substance abuse: cocaine and amphetamine
- High blood pressure
- Cigarette smoking
- High cholesterol
- Diabetes
- Obstructive sleep apnea
- heart failure, heart defects, heart infections and abnormal heart rhythm
- Personal and family history of stroke
- Age more than 55 years
- Male sex
- Birth control pills
What are the complications?
- Paralysis
- Difficulty in talking or swallowing
- Memory loss
- Comprehension problems
- Emotional issues
- Pain
- Behavioral changes
Can stroke be prevented?
- Controlling blood pressure
- Lowering cholesterol
- Decreasing saturated fat in diet
- Quitting tobacco
- Controlling diabetes
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Regular exercise
- Alcohol in moderation
- Treatment of obstructive sleep apnea
- Avoiding illegal drugs
Are there any preventive medications?
- Blood thinners
- Medications to lower cholesterol


