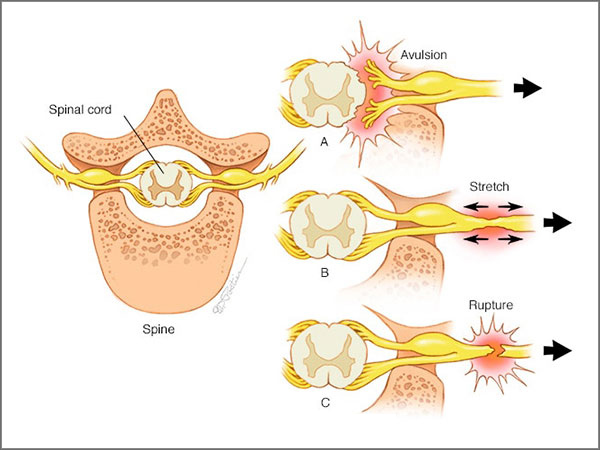
What is brachial plexus?
Brachial plexus is a network of neurons that sends signals from the spinal cord to shoulder arm and hand. It is injured when the nerves are stretched, compressed, ripped apart or torn away from the spinal cord. Severe brachial plexus injuries can leave the arm paralyzed. Surgical procedures such as nerve grafts, nerve transfer and muscle transfer can help restore function
What are the symptoms?
- Symptoms vary depending on the severity of the injuries
- Mild injuries called stingers
- Electric shock or burning sensation in arm
- Numbness or weakness in arms
- These symptoms are short lived
- Severe injuries
- Weakness or inability to use certain muscles
- Complete lack of movement
- Severe pain
What are the causes?
- Contact sports
- Difficulty delivery (Erb’s palsy)
- Trauma
- Tumors and post treatment after cancer
Complications of brachial plexus injuries:
- Joint stiffness
- Pain and numbness
- Muscle atrophy and permanent disability
Diagnosis:
- Electromyography to test the electrical activity in one’s muscle
- Nerve conduction studies provides information regarding the integrity of the nerve
- MRI shows the extent of damage to brachial plexus and the surrounding blood vessels
Treatment:
- It depends on several factors including the severity of injury, type of injury and length of time since the injury
- Mild injuries do not require any treatment
- Physical therapy to avoid muscle wasting and stiff joints
- Surgery to repair brachial plexus nerves
- Nerve graft: the damaged part of the nerve is removed and is replaced by a nerve harvested from other parts
- Nerve transfer: here a less important nerve is connected to a more important non functioning nerve
- Muscle transfer: here a less important muscle is transferred to an area with an important movement.


